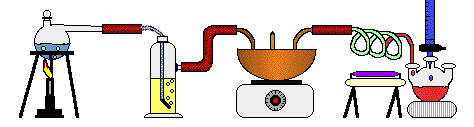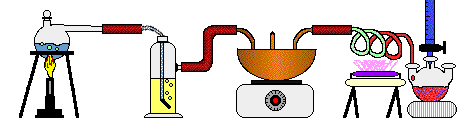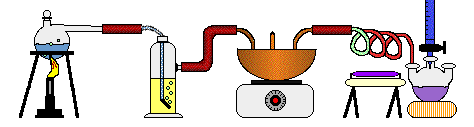
1. On paper.
2. During evaporation dissolved substances in the water are removed (like salt, heavy metals and minerals). When water is running through the ground suspended particles are filtered out through the sand and rocks. Also, when water is in its groundwater stage, bacteria in the dirt kill other organic substances that are found in the water.
3. Aluminum hydroxide, which is a sticky, jelly-like material, is used during water treatment processes. It is mixed with water and clings to the suspended particles in there. The water then sits for a bit, allowing the aluminum hydroxide drop to the bottom with the suspended particles. This process is called flocculation.
4. Calcium oxide, or lime, is a basic substance sometimes added to further purify water. It helps because it neutralizes the slight acidity in water that is being treated.
5. In the final steps of water treatments sometimes 1 ppm of fluoride is added to the water during a process called fluoridation. This substance helps reduce teeth decay and is also found in toothpaste.
6. Chlorinated drinking water is less likely to have bacteria in it because chlorine kills those substances. Also, even if some type of bacteria-fighting substance is added, it may not continue to fight off the bacteria like chlorine does.
7. Yes, there is. Chlorine in water sometimes reacts with organic compounds called and if the concentration of these compounds gets too high iy van be harmful to human health. Some of these compounds are called trihalomethanes, and include chloroform, which can cause cancer.
8. Even if water in a stream appears clear and safe to drink, bacterial substances are most likely present. Therefore chlorine is needed to kill those substances and make it safe to drink.
9. Two alternatives to chlorination would be charcoal filtration and using ultraviolet light. Charcoal filtration would properly filter out most organic compounds, but it is a very expensive process to uphold. Ultraviolet light eliminates bacteria, but cannot protect the water once it leaves the plant. It is also dangerous if not handled properly.
18. If evaporation stopped, then the dissolved liquids in water would not be able to be removed naturally. Also, the volume of rivers, lakes, streams, and oceans would go up because there is no place for the water to go. Another problem would be the lack of rain. With no water rising into the atmosphere, no clouds can form to create rain. Evaporation is a very crucial and helpful step in nature’s water cycle.
19. If water was not present in all 3 stages on earth, there would be no point for the water cycle. The water cycle is basically water changing between its forms, but without them this cycle is useless.
20. It limits it because even though they are dangerous we still need the chlorine. The effects if THMs is not huge compared to the need of chlorine.
21. The steps are similar because we have evaporation, which is like distillation, filtration through the sand, and there is probably charcoal in ground as well.
22. I don’t know.